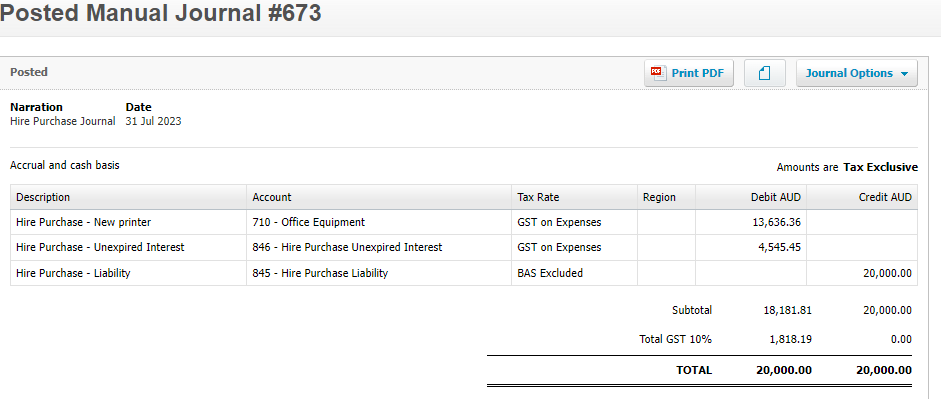
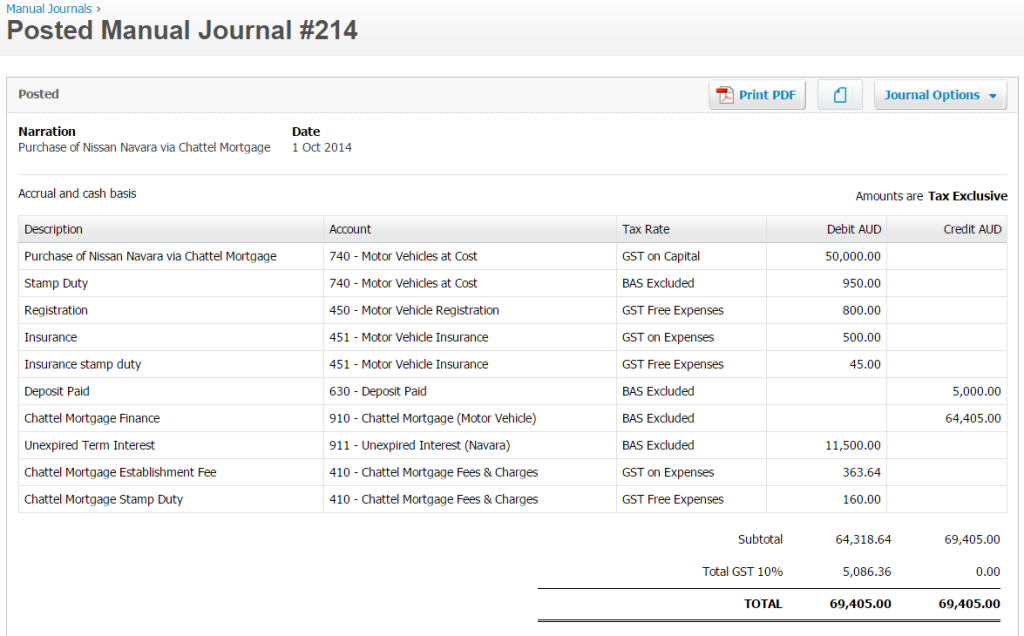
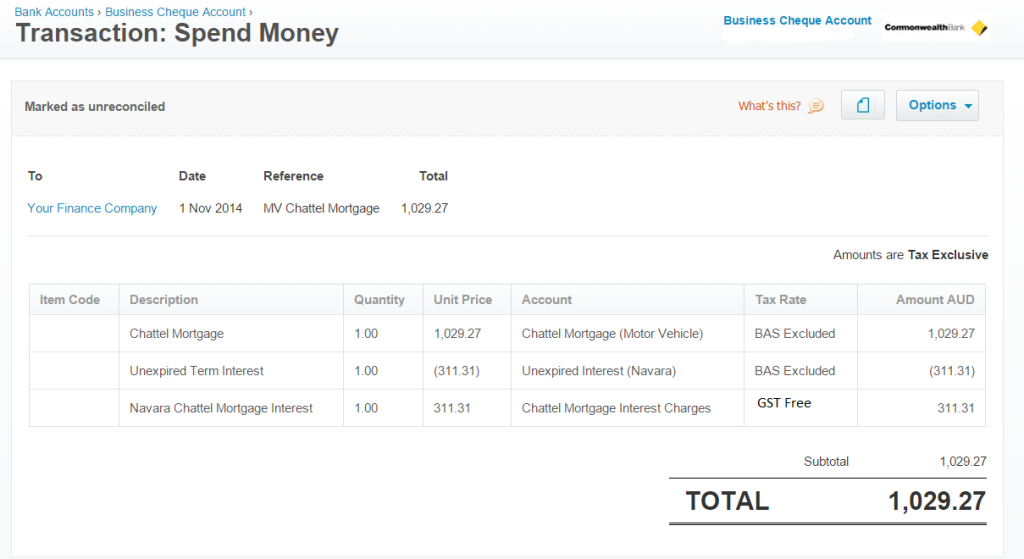
Why has my PAYG Withholding Cycle Changed?
If you’re an employer, your PAYG withholding (PAYGWH) cycle might change depending on how much you withheld in the prior financial year. The ATO will advise you about this change in April each year via a written letter. The cycle change will occur on 1 July of the next financial year.
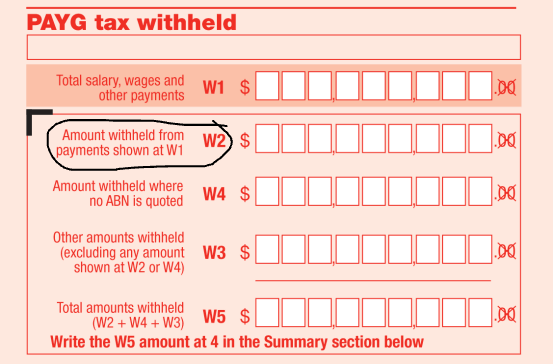
As a small withholder (small employer) you pay PAYGWH with GST and other taxes in your quarterly BAS. But, the ATO can switch your PAYGWH to monthly if, in the last financial year,
you withheld $25,001 to $1,000,000 from employee wages
These employers are called “medium withholders”.
If that’s you, you must lodge and pay a monthly Instalment Activity Statement (IAS) by the 21st of each month. For example, PAYGWH for July is due by August 21st.
If you withheld over $1 million last financial year, you’re a “large withholder”.
Large employers have specific dates to pay PAYGWH and get special payment reference numbers (PRN). The ATO will provide you with these details. Remember, large withholders don’t report PAYGWH on their activity statement, but they should still match up their reported STP and paid amounts.
If the ATO changes your PAYGWH cycle, update your payroll software to meet the new deadlines.
If you think your PAYGWH for the next financial year will be below the thresholds mentioned above, you can ask to stay on your current PAYGWH cycle. You must do this within 14 days after getting the ATO’s letter about the cycle change. Complete this form and send it to the ATO (or your tax agent can help).
For more info, check out the ATO Annual Review of PAYG Withholding Cycles on the ATO website.
Why has my PAYG Withholding Cycle Changed? Read More »